NCCETC Leads Southeast Onsite Energy Technical Assistance Partnership to Elevate Industrial Clean Energy
 The North Carolina Clean Energy Technology Center (NCCETC) is poised to assist manufacturers and other large energy users across the Southeast integrate onsite energy technologies into their facilities. This regional resource is possible through the Southeast Onsite Energy Technical Assistance Partnership (TAP), led by NCCETC, with two partner universities; the University of Puerto Rico Mayagüez (UPRM) and Tennessee Tech University.
The North Carolina Clean Energy Technology Center (NCCETC) is poised to assist manufacturers and other large energy users across the Southeast integrate onsite energy technologies into their facilities. This regional resource is possible through the Southeast Onsite Energy Technical Assistance Partnership (TAP), led by NCCETC, with two partner universities; the University of Puerto Rico Mayagüez (UPRM) and Tennessee Tech University.
The Southeast Onsite Energy TAP is part of a network of 10 regional Onsite Energy TAPs created to help industrial facilities and other large energy users transition to clean energy, lower costs, reduce emissions and contribute to a clean energy economy through a new Onsite Energy Program hosted by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE).
 Isaac Panzarella, Associate Director at the NCCETC, is the director for the DOE Southeast Onsite Energy TAP. “The creation of the Onsite Energy TAPs will expand significantly on the work we were able to do to support manufacturers and other organizations through the Southeast CHP TAP, which played a crucial role in promoting greater adoption of clean and efficient energy in the industrial sector,” stated Panzarella.
Isaac Panzarella, Associate Director at the NCCETC, is the director for the DOE Southeast Onsite Energy TAP. “The creation of the Onsite Energy TAPs will expand significantly on the work we were able to do to support manufacturers and other organizations through the Southeast CHP TAP, which played a crucial role in promoting greater adoption of clean and efficient energy in the industrial sector,” stated Panzarella.
NCCETC previously led the DOE Southeast Combined Heat and Power Technical Assistance Partnership (CHP TAP). “The CHP TAP’s purpose was to transform the market for CHP, waste heat to power, and district energy technologies,” Panzarella said.
In response to the evolving needs of the industrial sector, the DOE’s Industrial Efficiency and Decarbonization Office (IEDO) expanded the TAP program to encompass a broader spectrum of onsite energy technologies and emphasize the integration of technology as a key economic driver for end users.
Why Onsite Energy?
 Onsite energy refers to the generation and storage of electric and thermal energy directly at the location where it is consumed. Onsite energy technologies can include but are not limited to battery storage, district energy, fuel cells, geothermal systems, CHP, industrial heat pumps, renewable fuels, solar photovoltaics (PV), solar thermal, thermal storage, wind power and other distributed energy solutions.
Onsite energy refers to the generation and storage of electric and thermal energy directly at the location where it is consumed. Onsite energy technologies can include but are not limited to battery storage, district energy, fuel cells, geothermal systems, CHP, industrial heat pumps, renewable fuels, solar photovoltaics (PV), solar thermal, thermal storage, wind power and other distributed energy solutions.
Panzarella highlighted the many benefits of onsite energy, stating, “When facilities amp up their onsite energy game, they’re able to decarbonize onsite energy consumption and increase operational flexibility to gain better control over outages and reliability challenges.” He further explained that onsite energy affords facilities the ability to strategically generate and store energy to reduce demand on the grid at the most economically advantageous times, leading to cost savings.
Producing and storing electricity and heat directly at a facility offers financial savings, reduces uncertainty associated with fuel costs, and enhances control over the integration of clean energy into processes. Onsite energy not only improves efficiency but also cuts operating costs by capturing usable energy that would otherwise be wasted.
The adoption of clean energy resources at the facility level contributes to industrial decarbonization efforts. Utilizing clean onsite energy technologies provides industrial facility owners with a viable path towards lower emissions and decreased dependence on fossil fuels achieved by generating electricity and heat from flexible, reliable and effective energy resources, such as:
 Battery Storage
Battery Storage
Battery storage systems enable users to store electricity onsite and use it as needed. This energy can be used to supplement supply when the grid is experiencing an outage and when demand is driving the cost higher.
Renewable Fuels
Biodiesel, ethanol, hydrogen, biogas, renewable natural gas and renewable diesel are all examples of renewable fuel sources. Renewable fuels help reduce emissions and cut down on traditional fuel consumption.
Combined Heat and Power
CHP, or cogeneration, represents an energy-efficient technology that produces electricity while harnessing otherwise wasted heat to supply valuable thermal energy for heating or cooling, all from a single fuel source. As the electricity is generated onsite, CHP minimizes fuel requirements and eliminates transmission and distribution losses associated with electricity traveling through power lines.
Learn more about the various onsite energy technologies from the DOE’s Better Building Solution Center Onsite Energy Program website.
How Can an Onsite Energy TAP Help You?
The Onsite Energy TAPs offer specialized, regionally specific services to help facilities nationwide adopt the latest onsite energy technologies. These services include:
- Technical Assistance: Evaluate sites for opportunities to implement onsite energy technologies and provide advanced services throughout the entire process, from screening to installation, operation, and maintenance.
- End User Engagement: Collaborate with organizations representing end-users to promote onsite energy as a cost-effective means of transitioning to a clean energy economy.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Interact with key stakeholders, such as utilities and policymakers, to identify and overcome barriers to onsite energy through unbiased, fact-based education.
 DOE’s Onsite Energy Program employs a regional TAP model, ensuring that end users receive tailored guidance and support aligned with local considerations as they transition to clean energy. TAPs offer specialized technical assistance tailored to the unique needs of organizations, providing insights into incentives, programs and policies relevant to their specific situations.
DOE’s Onsite Energy Program employs a regional TAP model, ensuring that end users receive tailored guidance and support aligned with local considerations as they transition to clean energy. TAPs offer specialized technical assistance tailored to the unique needs of organizations, providing insights into incentives, programs and policies relevant to their specific situations.
These TAPs play a comprehensive role, evaluating sites for opportunities to implement onsite energy technologies and delivering advanced services to optimize economic impact while mitigating risks throughout the entire process—from initial screening to installation, operations, and maintenance.
In addition to their hands-on assistance, TAPs conduct education and outreach initiatives. They actively engage with policymakers, utilities and other key stakeholders to identify pathways that can expedite the integration of onsite clean energy technologies. These efforts include developing regional resources, sharing best practices and establishing partnerships to drive decarbonization within the U.S. industrial sector.
To uphold the highest standards of technical assistance, the TAPs receive support from three DOE national laboratories—namely, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. These laboratories bring subject matter expertise in onsite energy deployment, ensuring consistent and top-quality technical assistance across the program.
The 10 regional Onsite Energy TAPs cover all 50 states, Guam, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
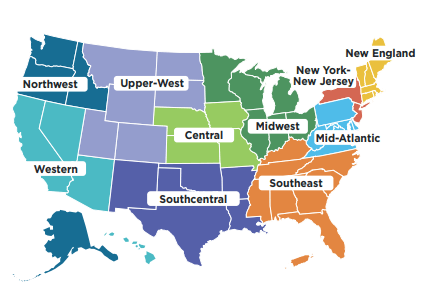
For more information visit IEDO’s Onsite Energy TAPs webpage or download this fact sheet.
The Onsite Energy Program and Technical Assistance Partnerships (TAPs) are overseen and funded by the U.S. Department of Energy Industrial Efficiency and Decarbonization Office.