The 50 States of Grid Modernization: Grid Modernization Action Increases by 60% in 2018
Raleigh, N.C. – (February 7, 2019) The N.C. Clean Energy Technology Center (NCCETC) released its 2018 annual review and Q4 2018 update edition of The 50 States of Grid Modernization. The quarterly series provides insights on state regulatory and legislative discussions and actions on grid modernization, utility business model and rate reforms, energy storage, microgrids, and demand response.
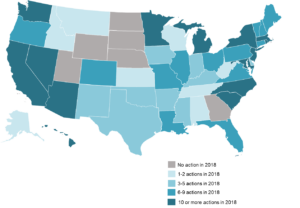
The report finds that 44 states and the District of Columbia took actions related to grid modernization during 2018 (see figure below), with the greatest number of actions relating to energy storage deployment, advanced metering infrastructure rules, utility business model reforms, smart grid deployment, and distribution system planning.
2018 Legislative and Regulatory Action on Grid Modernization
The report highlights ten of the top grid modernization trends of 2018:
- States and utilities undertaking distribution system planning efforts;
- States studying the value of energy storage and policy options to expand deployment;
- Regulators rejecting and scaling back utility grid modernization investments;
- Growing movement toward performance-based regulation;
- Utilities requesting special ratemaking treatment for grid investments;
- States concluding grid modernization investigations and identifying next steps;
- Regulators establishing clear standards for energy storage interconnection;
- States considering rules for access to customer energy usage data;
- Utilities proposing advanced metering infrastructure opt-out tariffs and fees; and
- Wholesale market operators expanding opportunities for energy storage participation.
“Grid modernization activity skyrocketed in 2018, as states addressed several different aspects of grid modernization simultaneously,” noted Autumn Proudlove, lead author of the report and Senior Manager of Policy Research at NCCETC. “We’re seeing many states tackle grid modernization issues in a very comprehensive way, not only looking at technology deployment, but also considering planning processes, utility business model reforms, and rate structures.”
A total of 460 grid modernization actions were taken during 2018, representing a 60% increase in activity over 2017 (288 actions). The report notes that ten of the most active states in 2018 for grid modernization were:
- New York where regulators adopted an energy storage target and policy roadmap, as well as a compensation tariff for renewable generators paired with energy storage;
- Nevada, where regulators approved distribution system planning rules, addressed energy storage interconnection issues, and completed an energy storage study;
- Hawaii, where utilities proposed an integrated grid planning process and several grid investments, while legislators initiated the creation of a microgrid services tariff;
- New Jersey, where lawmakers adopted an energy storage target and initiated an energy storage study, while utilities proposed major grid investments;
- California, where utilities requested approval for several storage and demand response projects and regulators considered energy storage rebates, time-varying rates, and distribution planning;
- Ohio, where the Commission completed its PowerForward grid modernization investigation and opened three new related proceedings, while utilities proposed major grid investments;
- Massachusetts, where lawmakers adopted a clean peak standard and expanded the state’s storage target, while regulators issued a decision on utility grid modernization plans;
- Michigan, where the Commission published a report on performance-based regulation and considered distribution system planning rules and data access standards;
- Minnesota, where regulators approved interconnection standards for energy storage and considered integrated distribution planning requirements; and
- Arizona, where the Commission considered several energy modernization issues and worked to develop interconnection standards for energy storage and innovative utility rate designs.
“At least 36 states considered actions related to energy storage in 2018, highlighting the key role of distributed energy resources in grid modernization,” said Achyut Shrestha, Project Manager at NCCETC. “States took a variety of actions related to storage in 2018, from efforts to study and plan for storage deployment to establishing procurement targets and incentives in order to drive the market forward.”
In Q4 2018, 39 states and D.C. took some type of action on distributed solar policy or rate design. A total of 280 actions were tracked in Q4.
View the 50 States of Grid Mod Q4 2018 annual review and update Executive Summary
View and Purchase the 50 States of Grid Mod Q4 2018 annual review and update FULL Report
View other 50 States Reports – Solar, Grid Modernization and Electric Vehicles
ABOUT THE N.C. CLEAN ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CENTER
The N.C. Clean Energy Technology Center, as part of the College of Engineering at North Carolina State University, advances a sustainable energy economy by educating, demonstrating and providing support for clean energy technologies, practices and policies. It serves as a resource for innovative, sustainable energy technologies through technology demonstration, technical assistance, outreach and training. For more information about the N.C. Clean Energy Technology Center, visit: http://www.nccleantech.
MEDIA CONTACT: Shannon Helm, NCCETC, shannon_helm@ncsu.edu, 919-423-8340